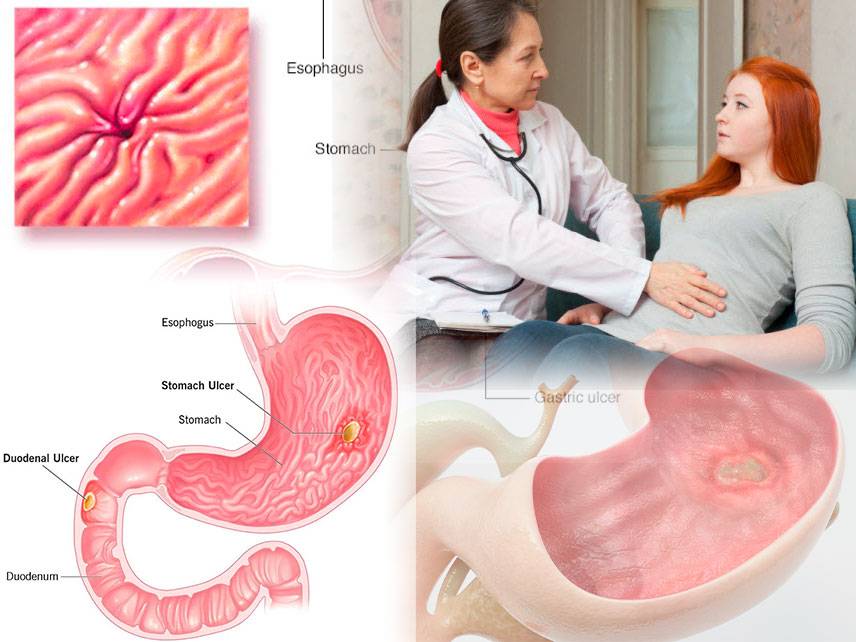
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a common condition in which painful sores form in the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus. These sores, also called ulcers, can cause burning pain and interfere with normal digestion. PUD is a serious condition that can lead to complications if it’s not treated.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of PUD is burning pain in the abdomen. This pain may come and go, and it can vary in intensity. Other symptoms include:
-
A feeling of fullness or bloating
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Weight loss
-
Loss of appetite
-
Acid reflux or heartburn
-
Dark or bloody stools
-
Unexplained fatigue
Causes
The exact cause of PUD is unknown, but most cases are believed to be caused by an infection with a bacteria called Helicobacter pylori. This bacteria can cause inflammation in the stomach and small intestine, leading to the formation of ulcers.
Risk Factors
There are certain factors that can increase your risk of developing PUD. These include:
-
Smoking
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
-
Stress
-
Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
A family history of PUD
-
Age (PUD is more common in people over the age of 50)
Prevention
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing PUD. These include:
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
-
Eating a healthy diet
-
Taking steps to reduce stress
-
Talking to your doctor about medications that could increase your risk of PUD
Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have PUD, it’s important to talk to your doctor. Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and review your medical history. They may order tests to confirm a diagnosis of PUD, including a blood test, stool test, or endoscopy.
Treatment
Treatment for PUD depends on the severity of the condition. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing stress. If your condition is caused by an infection with H. pylori, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove an ulcer that doesn’t respond to medications.
Coping and Support
Living with PUD can be difficult. It’s important to talk to your doctor about ways to cope with the condition. Your doctor may refer you to a support group or therapist to help you manage your symptoms.
Complications
If PUD is left untreated, it can lead to serious complications. These include:
-
Bleeding
-
Perforation (a hole in the stomach or intestine)
-
Blockage of the intestine
-
An increased risk of stomach cancer
Living with Peptic Ulcer Disease
Living with PUD can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to manage the condition. It’s important to take your medications as prescribed by your doctor and make lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing stress. It’s also important to eat a healthy diet and get regular exercise. By following your doctor’s advice and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can help manage your condition and reduce your risk of complications.