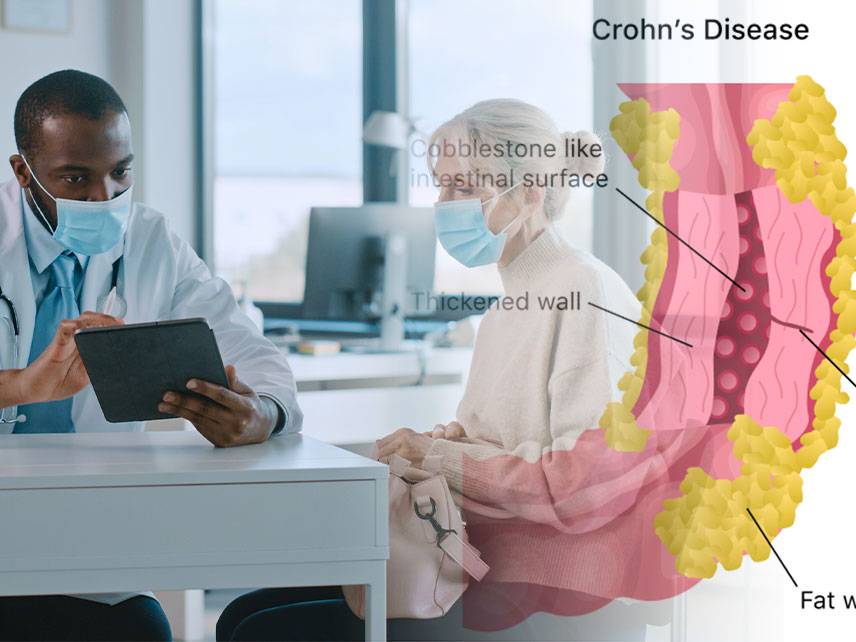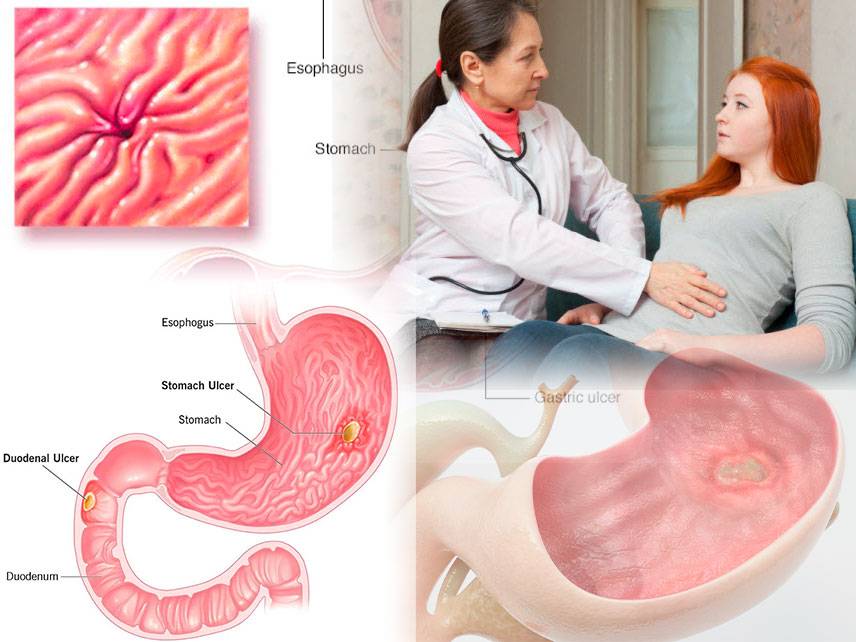
Gastroenteritis: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment.
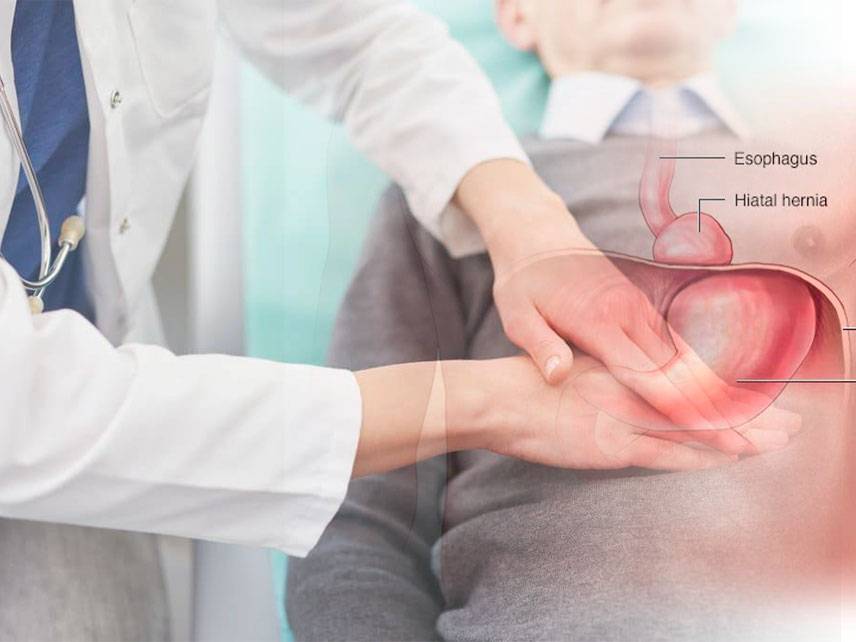
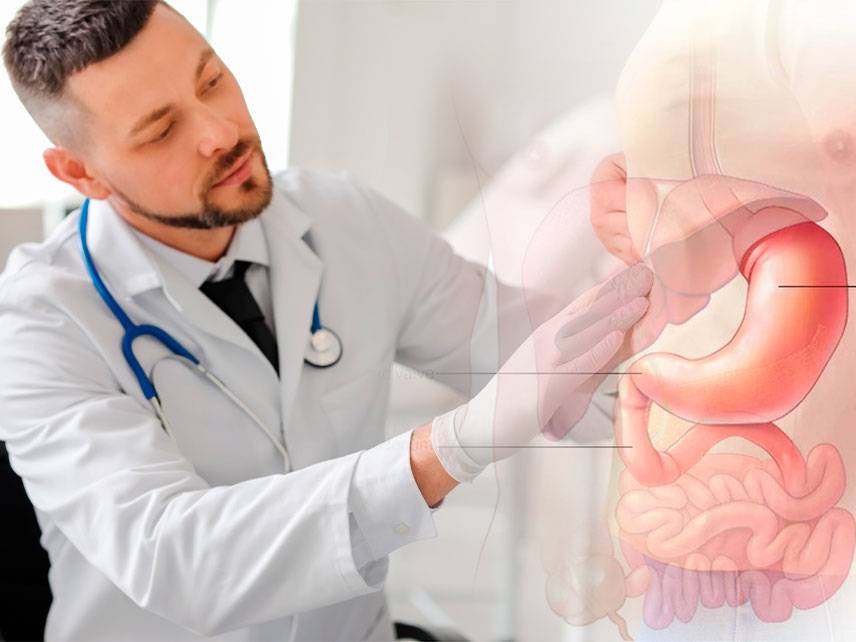
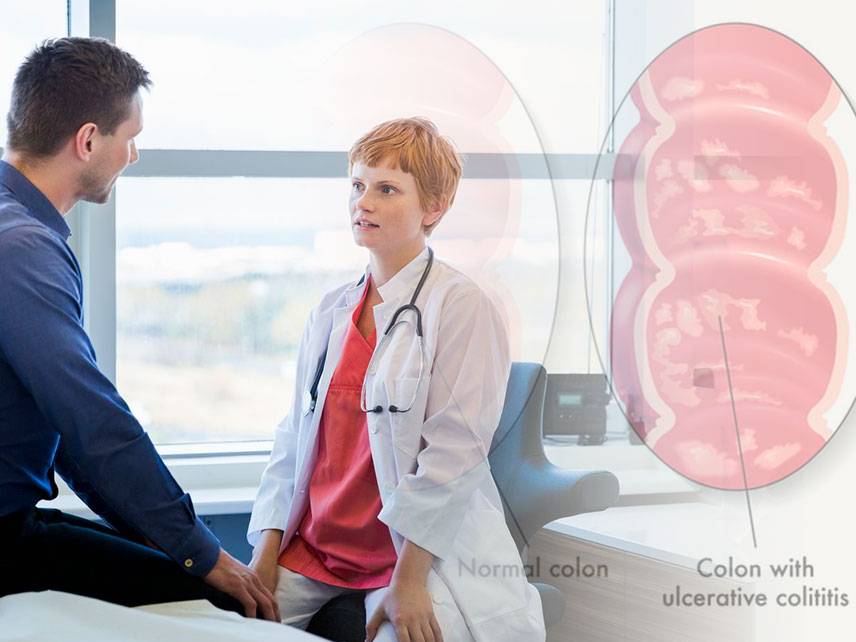
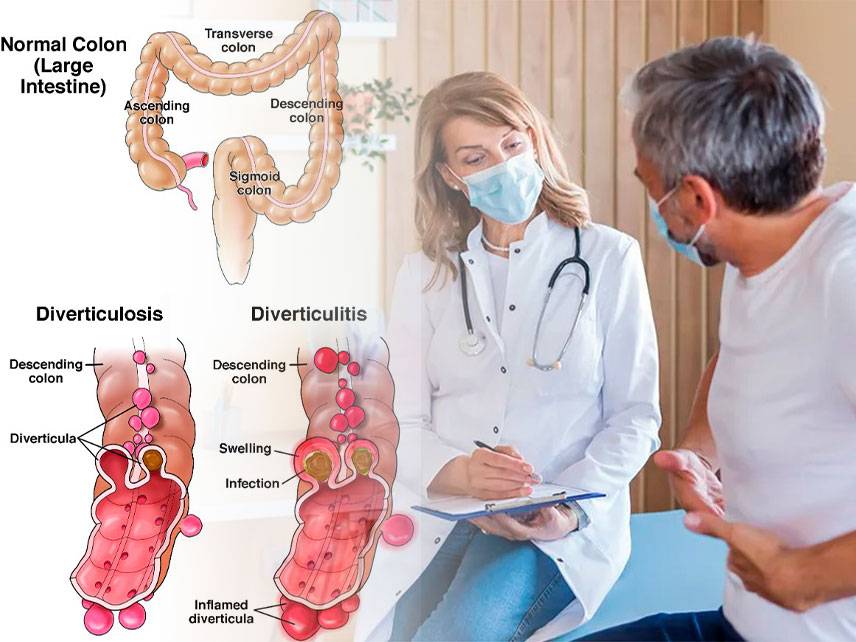
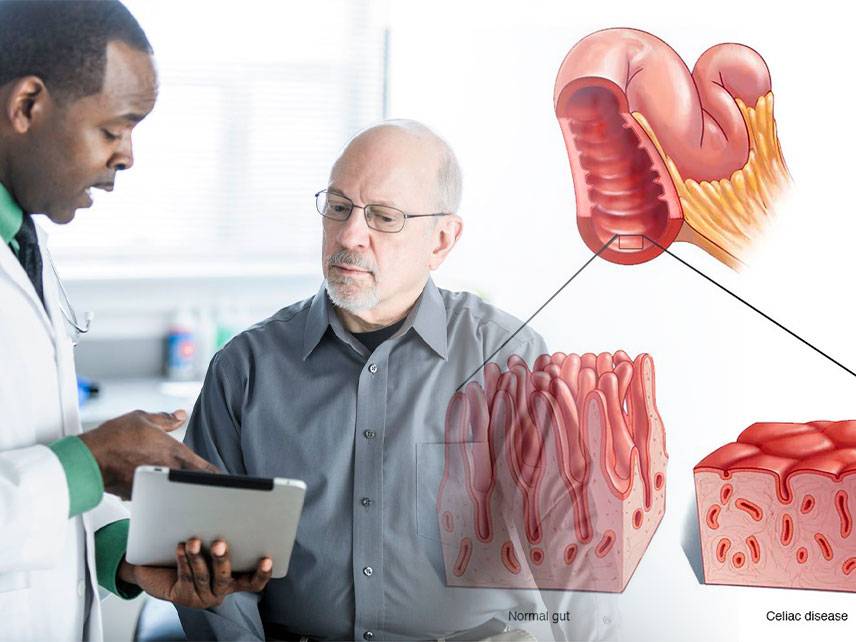
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the digestive system, especially of the stomach and intestines. It is typically caused by a virus, bacteria, or parasite and can be mild or severe. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Diagnosis is typically made by taking a medical history and physical exam, followed by laboratory tests and imaging studies. Treatment may involve antibiotics, antidiarrheal medications, and supportive care. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. Prevention is best achieved by practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding contaminated food and water.